Project Management Approach
Intelliinfotech's methodology and project management system can be applied to any IT project.
To make the work processes effective and efficient, we follow well-known and established
Methodologies, use modern Project Management Instruments and offer flexible ways
of Project Management Organization.
Methodologies
The software development methodologies that Intelliinfotech uses are based on iterative
/ incremental methodology, since this is considered a step up from the traditional
Waterfall model. Depending on the specifics of each project and client, we use both
Formal and Agile methods of software development process organization at Intelliinfotech
Formal Methods
Rational Unified Process (RUP)
|
As far as iterative software development methodologies are concerned, the RUP development
process is divided into iterations which are grouped into 4 phases. Each iteration
includes some workflow parts. We assume that according to RUP, a process is measured
in two dimensions:
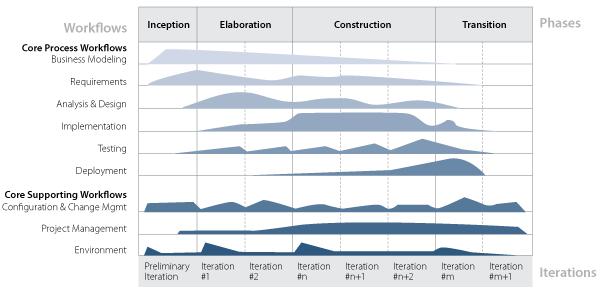
Time – Iterations:
- Inception: stage of project analysis
- Elaboration: working out a detailed
development plan
- Construction – development of
the project
- Transition – software testing
and customer delivery
|
|
|
Engineering disciplines:
1. Business modeling – establishment of a better understanding and communication channels between business (organization or client company in which the software will be used) and software engineering. This includes understanding the structure, further development goals, current problems, and possible improvements of the target organization.
2. Requirements – listening to clients’ requests and transforming them into sets of requirements, thus creating technical specifications.
3. Analysis and design –presenting an outline of how the source code will be structured and written, representing the future components in the implementation.
4. Implementation - realizing entire systems through the implementation of individual components.
5. Test – verifying the interaction between objects and the proper integration of software components, ensuring that all requirements have been correctly implemented, bugs are fixed, tested, and closed.
6. Deployment – producing successful product releases, delivering the software to end users, installing, and providing assistance.
|
Supporting disciplines:
1. Change management – this includes configuration management (systematic product structuring, keeping documents and models under version control), change request management (keeping track of the changing requests), status and measurement management (tracking statuses of change requests – new, logged, approved, assigned or complete, its priority levels, etc.).
2. Project Management – two-level planning: The software development plan (general, The Phase plan) and The Iteration plan.
3. Environment – providing the software development organization with the necessary processes and tools, the software development environment
|
This is generally used when:
- The level of criticality is high - is used when even minor permanent errors are not acceptable (surgery software)
- Requirements are defined clearly and can be changed in exceptional cases
- Separate projects or tasks need to be developed, for which an exact time frame can be measured
This methodology can be applied to both the fixed price model and the time and materials payment model.
|